PyTorch 源码阅读笔记(7):TorchDynamo
TorchDynamo
关于 TorchDynamo
torchdynamo 为 PyTorch 2.0 的新功能,可以在不修改代码的情况下,对大部分模型提速,基本的使用方式如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import torch
def fn(x, y):
a = torch.cos(x).cuda()
b = torch.sin(y).cuda()
return a + b
new_fn = torch.compile(fn, backend="inductor")
input_tensor = torch.randn(10000).to(device="cuda:0")
a = new_fn(input_tensor, input_tensor)
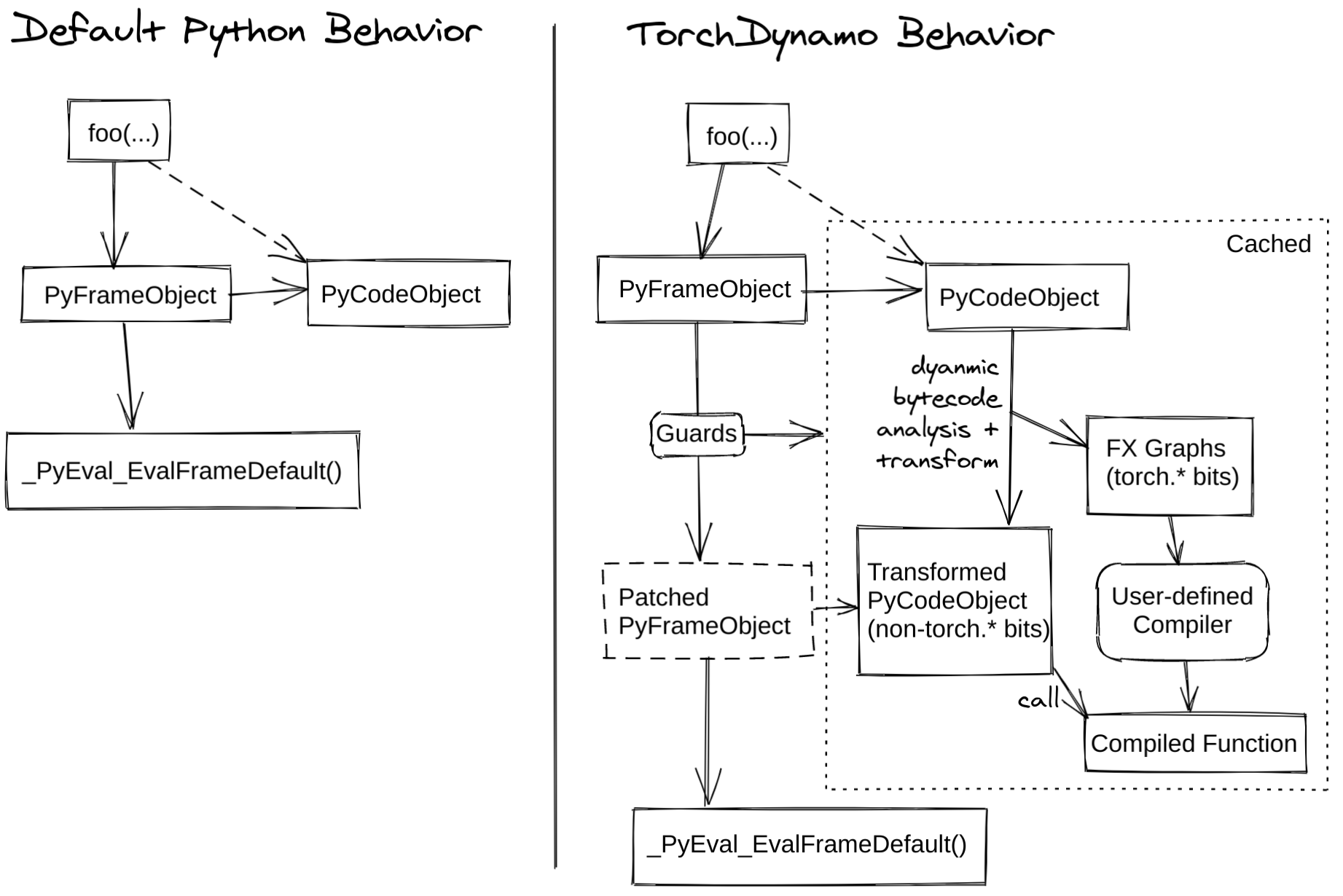
TorchDynamo 原理
官方给出的 TorchDynamo 原理图如下
| 涉及到关于 Python 编译运行的内容参考 [python 编译运行过程]([Python 代码编译运行过程(1):编译过程 | K’s blog (luokai.tech)](https://luokai.tech/posts/python/python_compile/) |
字节码优化
torchdynamo 通过捕捉 python 的 frame object 进行字节码优化,运行如下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from torch._dynamo import optimize
import torch._dynamo.config
import logging
torch._dynamo.config.log_level = logging.INFO
torch._dynamo.config.output_code = True
@optimize()
def toy_example(a, b):
a *= 10
b = b + 1
return b
for _ in range(100):
toy_example(torch.randn(10), 9527)
输出可以看到 toy_example 代码块的原始字节码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
torch._dynamo.convert_frame: [INFO] ORIGINAL BYTECODE toy_example <ipython-input-5-1ef27a145933> line 7
9 0 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
2 LOAD_CONST 1 (10)
4 INPLACE_MULTIPLY
6 STORE_FAST 0 (a)
10 8 LOAD_FAST 1 (b)
10 LOAD_CONST 2 (1)
12 BINARY_ADD
14 STORE_FAST 1 (b)
11 16 LOAD_FAST 1 (b)
18 RETURN_VALUE
修改后的字节码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
torch._dynamo.convert_frame: [INFO] MODIFIED BYTECODE toy_example <ipython-input-5-1ef27a145933> line 7
7 0 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (__compiled_fn_1)
2 LOAD_FAST 0 (a)
4 CALL_FUNCTION 1
6 POP_TOP
8 LOAD_CONST 3 (9528)
10 RETURN_VALUE
对比字节码修改的地方,可以发现针对 tensor 的操作指向了 __compiled_fn_1(对 tensor 执行的编译后的核函数),同时还把函数内的 b + 1 结果当成常量处理,提高了效率。
查看 pytorch 源码,字节码替换的步骤发生在下面代码里
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
...
def transform(instructions, code_options):
nonlocal output
tracer = InstructionTranslator(
instructions,
code,
locals,
globals,
builtins,
code_options,
compiler_fn,
one_graph,
export,
mutated_closure_cell_contents,
)
tracer.run()
output = tracer.output
assert output is not None
assert output.output_instructions
instructions[:] = output.output_instructions
code_options.update(output.code_options)
...
def step(self):
"""Process exactly one instruction, return False we should exit"""
assert isinstance(self.instruction_pointer, int)
inst = self.instructions[self.instruction_pointer]
self.current_instruction = inst
self.instruction_pointer += 1
if self.instruction_pointer < len(self.instructions):
self.next_instruction = self.instructions[self.instruction_pointer]
else:
self.instruction_pointer = None
self.next_instruction = None
if inst.starts_line and self.lineno != inst.starts_line:
self.lineno = inst.starts_line
log.debug(f"TRACE starts_line {self.f_code.co_filename}:{self.lineno}")
if len(self.stack) == 0 and self.should_compile_partial_graph():
self.checkpoint = inst, self.copy_graphstate()
log.debug(f"TRACE {inst.opname} {inst.argval} {self.stack}")
try:
if not hasattr(self, inst.opname):
unimplemented(f"missing: {inst.opname}")
getattr(self, inst.opname)(inst)
return inst.opname != "RETURN_VALUE"
except BackendCompilerFailed:
raise
except Unsupported as exc:
exc.real_stack.append(self.frame_summary())
if self.empty_checkpoint():
raise
log.debug("step triggered compile", exc_info=True)
except Exception as exc:
real_stack = getattr(exc, "real_stack", [])
real_stack.append(self.frame_summary())
exc.real_stack = real_stack # type: ignore[attr-defined]
raise
# generate code from checkpoint
assert not self.output.output_instructions
assert self.checkpoint is not None
continue_inst, state = self.checkpoint
self.restore_graphstate(state)
self.output.compile_subgraph(
self,
partial_convert=True,
reason=GraphCompileReason("step_unsupported", [self.frame_summary()]),
)
self.output.add_output_instructions(
[create_jump_absolute(continue_inst)] + self.instructions
)
...
上面代码中,每一步都会根据原始字节码列表索引 instruction_pointer 获取当前的指令,然后 self.instruction_pointer += 1,self.output.compile_subgraph 方法内会在 output_instructions 列表新增一个指令,回到step函数, self.output.add_output_instructions 方法给 output_instructions extend 对当前而言的下一个指令 + 原始的完整指令列表。这一系列步骤一直重复到 self.instruction_pointer 超过原始指令长度便结束,然后整体清除一下 output_instructions 被跳过了的指令,就得到了新的指令列表。
小结 & 待补充
本文粗略地看了一下 TorchDynamo,该模块类似一个编译器,在运行时把 Python 字节码 stack 编译成新的字节码 stack,不仅实现了大幅度的提速(gpu 等加速卡上面还涉及到其他模块),还完全兼容之前版本的代码(很想@一下tensorflow)。
TorchDynamo 涉及到大量编译相关的底层细节,想要完全弄清楚还需要大量的学习和时间投入,有时间和能力时再逐步补充。